

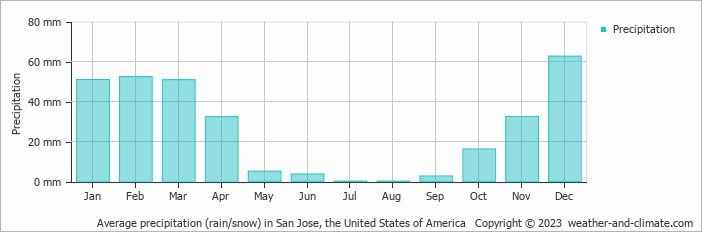
Īccording to the NOAA Drought Task Force report of 2014, the drought is not part of a long-term change in precipitation and was a symptom of the natural variability, although the record-high temperature that accompanied the recent drought may have been amplified due to human-induced global warming. While variability in climate patterns are a natural occurrence, AR6 concluded that human influences have increased the chance of compound extreme weather events, specifically "increases in the frequency of concurrent heatwaves and droughts on the global scale" with high confidence. See also: Southwestern North American megadroughtĪccording to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change or IPCC, their Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) on the effects of climate change revealed a number of scientifically supported claims on what is to become the future of the earth. This delicate balance means that a dry rainy season can have lasting consequences. Precipitation in California occurs mostly from November to May, with the vast majority of rain and snowfall across the state occurring during the winter months. In addition to technical categories, the Governor Newsom administration introduced in 2023 the concept of a political drought, where state public policy actions would need to continue even after short-term drought conditions may have ameliorated. A meteorological drought may be short lived without causing disturbance but when longer lasting may enter other categories according to its impacts.
There are five major technical categories of drought: (1) Meteorological, (2) Agricultural, (3) Hydrological, (4) Socioeconomic, and (5) Ecological. California is not only the most populous state and largest agricultural producer in the United States, it is also the most biodiverse as such, drought in California can have a far reaching economic and environmental impacts. Since the California water supply is attained from numerous sources, fulfilled by varied and intricate weather patterns, there is no one cause of drought. The historical and ongoing droughts in California result from various complex meteorological phenomena, some of which are not fully understood by scientists.ĭrought is generally defined as "a deficiency of precipitation over an extended period of time (usually a season or more), resulting in a water shortage." Ī lack of rainfall (or snowfall) or precipitation in meager quantities, higher than average temperatures and dry air masses in the atmosphere commonly underlie drought conditions these natural factors are further complicated by increases in populations and water demands.
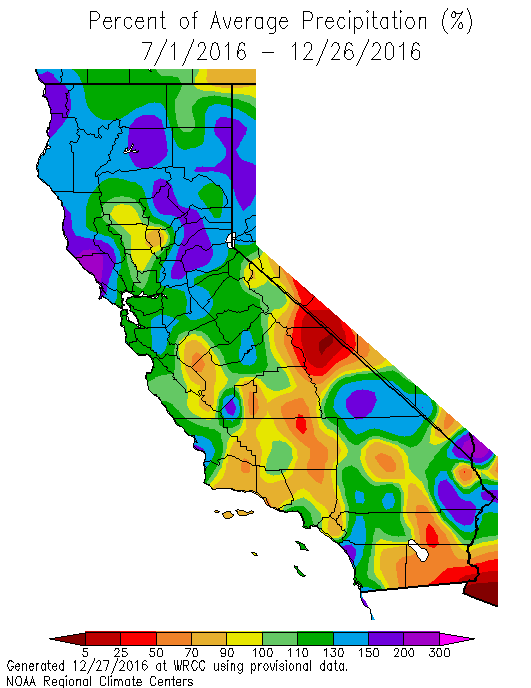
The data is processed in javascript and visualized here using HTML, CSS and javascript and the open source Plotly javascript graphing library.Percent area in U.S. You can hover (or click) on the graph to audit the data a little more clearly.ĭata is downloaded from the California Data Exchange Center website of the California Department of Water Resources using a python script. It also shows the present precipitation level and its percentile within the historical data for the day of the water year.

You can see the current water year plotted on this to show how it compares to historical values. The second graph shows the percentiles of precipitation over the course of the historical water year, spreading out like a cone from the start of the water year (October 1). The top graph is a histogram of water year precipitation totals on the specified date (in blue) as well as the precipitation total for the current water year in red. The visualization consists of two primary graphs both of which show the range of historical values for precipitation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
